Abstract
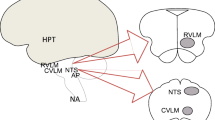
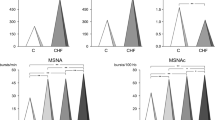
Sympathetic nerve activity has been reported to be increased in both humans and animals with chronic heart failure. One of the mechanisms believed to be responsible for this phenomenon is increased systemic and cerebral angiotensin II signaling. Plasma angiotensin II is increased in humans and animals with chronic heart failure. The increase in angiotensin II signaling enhances sympathetic nerve activity through actions on both central and peripheral sites during chronic heart failure. Angiotensin II signaling is enhanced in different brain sites such as the paraventricular nucleus, the rostral ventrolateral medulla and the area postrema. Blocking angiotensin II type 1 receptors decreases sympathetic nerve activity and cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex when therapy is administered to the paraventricular nucleus. Injection of an angiotensin receptor blocker into the area postrema activates the sympathoinhibitory baroreflex. In peripheral regions, angiotensin II elevates both norepinephrine release and synthesis and inhibits norepinephrine uptake at nerve endings, which may contribute to the increase in sympathetic nerve activity seen in chronic heart failure. Increased circulating angiotensin II during chronic heart failure may enhance the sympathoexcitatory chemoreflex and inhibit the sympathoinhibitory baroreflex. In addition, increased circulating angiotensin II can directly act on the central nervous system via the subfornical organ and the area postrema to increase sympathetic outflow. Inhibition of angiotensin II formation and its type 1 receptor has been shown to have beneficial effects in chronic heart failure patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACE:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
- AngII:
-
Angiotensin II
- AT1R:
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CHF:
-
Chronic heart failure
- CSAR:
-
Cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- IML:
-
Intermediolateral cell column
- i.v.:
-
Intravenous
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- NE:
-
Norepinephrine
- nNOS:
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- NTS:
-
Nucleus of the solitary tract
- PVN:
-
Paraventricular nucleus
- RVLM:
-
Rostral ventrolateral medulla
- SFO:
-
Subfornical organ
- SNA:
-
Sympathetic nerve activity
References
Penne EL, Neumann J, Klein IH, Oey PL, Bots ML, Blankestijn PJ (2009) Sympathetic hyperactivity and clinical outcome in chronic kidney disease patients during standard treatment. J Nephrol 22:208–215
Zhou Y, Xie G, Wang J, Yang S (2012) Cardiovascular risk factors significantly correlate with autonomic nervous system activity in children. Can J Cardiol 28:477–482
Akutsu Y, Kaneko K, Kodama Y et al (2008) Cardiac sympathetic nerve abnormality predicts ventricular tachyarrhythmic events in patients without conventional risk of sudden death. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35:2066–2073
Malpas SC, Ramchandra R, Guild SJ, McBryde F, Barrett CJ (2006) Renal sympathetic nerve activity in the development of hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 8:242–248
Hogarth AJ, Mackintosh AF, Mary DA (2007) The effect of gender on the sympathetic nerve hyperactivity of essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 21:239–245
Weck M (2007) Treatment of hypertension in patients with diabetes mellitus: relevance of sympathovagal balance and renal function. Clin Res Cardiol 96:707–718
Blankestijn PJ (2007) Sympathetic hyperactivity—a hidden enemy in chronic kidney disease patients. Perit Dial Int 27(Suppl 2):S293–S297
Blankestijn PJ (2004) Sympathetic hyperactivity in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:1354–1357
Joles JA, Koomans HA (2004) Causes and consequences of increased sympathetic activity in renal disease. Hypertension 43:699–706
Koomans HA, Blankestijn PJ, Joles JA (2004) Sympathetic hyperactivity in chronic renal failure: a wake-up call. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:524–537
Neumann J, Ligtenberg G, Klein II, Koomans HA, Blankestijn PJ (2004) Sympathetic hyperactivity in chronic kidney disease: pathogenesis, clinical relevance, and treatment. Kidney Int 65:1568–1576
Augustyniak RA, Tuncel M, Zhang W, Toto RD, Victor RG (2002) Sympathetic overactivity as a cause of hypertension in chronic renal failure. J Hypertens 20:3–9
Hasking GJ, Esler MD, Jennings GL, Burton D, Johns JA, Korner PI (1986) Norepinephrine spillover to plasma in patients with congestive heart failure: evidence of increased overall and cardiorenal sympathetic nervous activity. Circulation 73:615–621
Eisenhofer G, Friberg P, Rundqvist B et al (1996) Cardiac sympathetic nerve function in congestive heart failure. Circulation 93:1667–1676
Narkiewicz K, Pesek CA, van de Borne PJ, Kato M, Somers VK (1999) Enhanced sympathetic and ventilatory responses to central chemoreflex activation in heart failure. Circulation 100:262–267
Leimbach WN Jr, Wallin BG, Victor RG, Aylward PE, Sundlof G, Mark AL (1986) Direct evidence from intraneural recordings for increased central sympathetic outflow in patients with heart failure. Circulation 73:913–919
Esler M, Kaye D, Lambert G, Esler D, Jennings G (1997) Adrenergic nervous system in heart failure. Am J Cardiol 80:7L–14L
Floras JS (1993) Clinical aspects of sympathetic activation and parasympathetic withdrawal in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 22:72A–84A
Zucker IH, Wang W, Brandle M, Schultz HD, Patel KP (1995) Neural regulation of sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 37:397–414
Reid IA (1992) Interactions between ANG II, sympathetic nervous system, and baroreceptor reflexes in regulation of blood pressure. Am J Physiol 262:E763–E778
DiBona GF (2000) Nervous kidney. Interaction between renal sympathetic nerves and the renin-angiotensin system in the control of renal function. Hypertension 36:1083–1088
Petersson M, Friberg P, Eisenhofer G, Lambert G, Rundqvist B (2005) Long-term outcome in relation to renal sympathetic activity in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 26:906–913
Kaye DM, Lefkovits J, Jennings GL, Bergin P, Broughton A, Esler MD (1995) Adverse consequences of high sympathetic nervous activity in the failing human heart. J Am Coll Cardiol 26:1257–1263
Eckberg DL, Drabinsky M, Braunwald E (1971) Defective cardiac parasympathetic control in patients with heart disease. N Engl J Med 285:877–883
Packer M, Bristow MR, Cohn JN et al (1996) The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. U.S. Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group. N Engl J Med 334:1349–1355
Packer M, Coats AJ, Fowler MB et al (2001) Effect of carvedilol on survival in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 344:1651–1658
Ramchandra R, Hood SG, Watson AM, Allen AM, May CN (2012) Central angiotensin type 1 receptor blockade decreases cardiac but not renal sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure. Hypertension 59:634–641
Ding Y, Li YL, Zimmerman MC, Davisson RL, Schultz HD (2009) Role of CuZn superoxide dismutase on carotid body function in heart failure rabbits. Cardiovasc Res 81:678–685
Sun SY, Wang W, Zucker IH, Schultz HD (1999) Enhanced peripheral chemoreflex function in conscious rabbits with pacing-induced heart failure. J Appl Physiol 86:1264–1272
Kang YM, Gao F, Li HH et al (2011) NF-kappaB in the paraventricular nucleus modulates neurotransmitters and contributes to sympathoexcitation in heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 106:1087–1097
Ma X, Abboud FM, Chapleau MW (2001) A novel effect of angiotensin on renal sympathetic nerve activity in mice. J Hypertens 19:609–618
Kang YM, He RL, Yang LM et al (2009) Brain tumour necrosis factor-alpha modulates neurotransmitters in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 83:737–746
Gomes da Silva AQ, Xavier CH, Campagnole-Santos MJ et al (2012) Cardiovascular responses evoked by activation or blockade of GABA(A) receptors in the hypothalamic PVN are attenuated in transgenic rats with low brain angiotensinogen. Brain Res 1448:101–110
Dampney RA, Horiuchi J, Killinger S, Sheriff MJ, Tan PS, McDowall LM (2005) Long-term regulation of arterial blood pressure by hypothalamic nuclei: some critical questions. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 32:419–425
Llewellyn T, Zheng H, Liu X, Xu B, Patel KP (2012) Median preoptic nucleus and subfornical organ drive renal sympathetic nerve activity via a glutamatergic mechanism within the paraventricular nucleus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302:R424–R432
Shafton AD, Ryan A, Badoer E (1998) Neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus send collaterals to the spinal cord and to the rostral ventrolateral medulla in the rat. Brain Res 801:239–243
Tagawa T, Dampney RA (1999) AT(1) receptors mediate excitatory inputs to rostral ventrolateral medulla pressor neurons from hypothalamus. Hypertension 34:1301–1307
Kumagai H, Oshima N, Matsuura T et al (2012) Importance of rostral ventrolateral medulla neurons in determining efferent sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure. Hypertens Res 35:132–141
Guyenet PG (2006) The sympathetic control of blood pressure. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:335–346
Dampney RA (1994) Functional organization of central pathways regulating the cardiovascular system. Physiol Rev 74:323–364
Watson AM, Hood SG, May CN (2006) Mechanisms of sympathetic activation in heart failure. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 33:1269–1274
Zucker IH, Schultz HD, Li YF, Wang Y, Wang W, Patel KP (2004) The origin of sympathetic outflow in heart failure: the roles of angiotensin II and nitric oxide. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 84:217–232
Zucker IH, Pliquett RU (2002) Novel mechanisms of sympatho-excitation in chronic heart failure. Heart Fail Monit 3:2–7
Wang W, Chen JS, Zucker IH (1991) Carotid sinus baroreceptor reflex in dogs with experimental heart failure. Circ Res 68:1294–1301
Dibner-Dunlap ME, Thames MD (1989) Baroreflex control of renal sympathetic nerve activity is preserved in heart failure despite reduced arterial baroreceptor sensitivity. Circ Res 65:1526–1535
Liu JL, Murakami H, Sanderford M, Bishop VS, Zucker IH (1999) ANG II and baroreflex function in rabbits with CHF and lesions of the area postrema. Am J Physiol 277:H342–H350
Wang W, Zhu GQ, Gao L, Tan W, Qian ZM (2004) Baroreceptor reflex in heart failure. Sheng Li Xue Bao 56:269–281
Chua TP, Ponikowski P, Webb-Peploe K et al (1997) Clinical characteristics of chronic heart failure patients with an augmented peripheral chemoreflex. Eur Heart J 18:480–486
Zhu GQ, Gao L, Li Y, Patel KP, Zucker IH, Wang W (2004) AT1 receptor mRNA antisense normalizes enhanced cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats with chronic heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H1828–H1835
Wang WZ, Gao L, Wang HJ, Zucker IH, Wang W (2008) Interaction between cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex and chemoreflex is mediated by the NTS AT1 receptors in heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1216–H1226
Zhu GQ, Zucker IH, Wang W (2002) Central AT1 receptors are involved in the enhanced cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats with chronic heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 97:320–326
Wang W, Ma R (2000) Cardiac sympathetic afferent reflexes in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev 5:57–71
Wang W, Schultz HD, Ma R (1999) Cardiac sympathetic afferent sensitivity is enhanced in heart failure. Am J Physiol 277:H812–H817
Ma R, Zucker IH, Wang W (1997) Central gain of the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in dogs with heart failure. Am J Physiol 273:H2664–H2671
Wang W, Zucker IH (1996) Cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in dogs with congestive heart failure. Am J Physiol 271:R751–R756
Wang W (1998) Cardiac sympathetic afferent stimulation by bradykinin in heart failure: role of NO and prostaglandins. Am J Physiol 275:H783–H788
Ma R, Zucker IH, Wang W (1999) Reduced NO enhances the central gain of cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in dogs with heart failure. Am J Physiol 276:H19–H26
Li YF, Patel KP (2003) Paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and elevated sympathetic activity in heart failure: the altered inhibitory mechanisms. Acta Physiol Scand 177:17–26
Chatterjee K (2005) Neurohormonal activation in congestive heart failure and the role of vasopressin. Am J Cardiol 95:8B–13B
Goldsmith SR (2006) The role of vasopressin in congestive heart failure. Clevel Clin J Med 73(Suppl 3):S19–S23
Zucker IH, Wang W, Pliquett RU, Liu JL, Patel KP (2001) The regulation of sympathetic outflow in heart failure. The roles of angiotensin II, nitric oxide, and exercise training. Ann N Y Acad Sci 940:431–443
van de Wal RM, Plokker HW, Lok DJ et al (2006) Determinants of increased angiotensin II levels in severe chronic heart failure patients despite ACE inhibition. Int J Cardiol 106:367–372
Liu JL, Irvine S, Reid IA, Patel KP, Zucker IH (2000) Chronic exercise reduces sympathetic nerve activity in rabbits with pacing-induced heart failure: a role for angiotensin II. Circulation 102:1854–1862
Kleiber AC, Zheng H, Sharma NM, Patel KP (2010) Chronic AT1 receptor blockade normalizes NMDA-mediated changes in renal sympathetic nerve activity and NR1 expression within the PVN in rats with heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298:H1546–H1555
Roig E, Perez-Villa F, Morales M et al (2000) Clinical implications of increased plasma angiotensin II despite ACE inhibitor therapy in patients with congestive heart failure. Eur Heart J 21:53–57
Liu D, Gao L, Roy SK, Cornish KG, Zucker IH (2006) Neuronal angiotensin II type 1 receptor upregulation in heart failure: activation of activator protein 1 and Jun N-terminal kinase. Circ Res 99:1004–1011
Ganta CK, Lu N, Helwig BG et al (2005) Central angiotensin II-enhanced splenic cytokine gene expression is mediated by the sympathetic nervous system. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H1683–H1691
Lu N, Helwig BG, Fels RJ, Parimi S, Kenney MJ (2004) Central Tempol alters basal sympathetic nerve discharge and attenuates sympathetic excitation to central ANG II. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H2626–H2633
Wei SG, Yu Y, Zhang ZH, Weiss RM, Felder RB (2008) Angiotensin II-triggered p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates sympathetic excitation in heart failure rats. Hypertension 52:342–350
Fujisawa Y, Nagai Y, Lei B et al (2011) Roles of central renin-angiotensin system and afferent renal nerve in the control of systemic hemodynamics in rats. Hypertens Res 34:1228–1232
Gao L, Zhu Z, Zucker IH, Wang W (2004) Cardiac sympathetic afferent stimulation impairs baroreflex control of renal sympathetic nerve activity in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H1706–H1711
Yamazato M, Ohya Y, Nakamoto M et al (2006) Sympathetic hyperreactivity to air-jet stress in the chromosome 1 blood pressure quantitative trait locus congenic rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R709–R714
Huang C, Yoshimoto M, Miki K, Johns EJ (2006) The contribution of brain angiotensin II to the baroreflex regulation of renal sympathetic nerve activity in conscious normotensive and hypertensive rats. J Physiol 574:597–604
Gao L, Pan YX, Wang WZ et al (2007) Cardiac sympathetic afferent stimulation augments the arterial chemoreceptor reflex in anesthetized rats. J Appl Physiol 102:37–43
DiBona GF, Jones SY, Brooks VL (1995) ANG II receptor blockade and arterial baroreflex regulation of renal nerve activity in cardiac failure. Am J Physiol 269:R1189–R1196
Gao L, Schultz HD, Patel KP, Zucker IH, Wang W (2005) Augmented input from cardiac sympathetic afferents inhibits baroreflex in rats with heart failure. Hypertension 45:1173–1181
Ferguson AV, Washburn DL, Latchford KJ (2001) Hormonal and neurotransmitter roles for angiotensin in the regulation of central autonomic function. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 226:85–96
Li YF, Wang W, Mayhan WG, Patel KP (2006) Angiotensin-mediated increase in renal sympathetic nerve discharge within the PVN: role of nitric oxide. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R1035–R1043
Yu Y, Zhong MK, Li J et al (2007) Endogenous hydrogen peroxide in paraventricular nucleus mediating cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex and regulating sympathetic activity. Pflugers Arch 454:551–557
Zhang Y, Yu Y, Zhang F et al (2006) NAD(P)H oxidase in paraventricular nucleus contributes to the effect of angiotensin II on cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex. Brain Res 1082:132–141
Shi Z, Gan XB, Fan ZD et al (2011) Inflammatory cytokines in paraventricular nucleus modulate sympathetic activity and cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 203:289–297
Zheng H, Sharma NM, Liu X, Patel KP (2012) Exercise training normalizes enhanced sympathetic activation from the paraventricular nucleus in chronic heart failure: role of angiotensin II. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 303:R387–R394
Silva AQ, Santos RA, Fontes MA (2005) Blockade of endogenous angiotensin-(1–7) in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus reduces renal sympathetic tone. Hypertension 46:341–348
Zhong MK, Duan YC, Chen AD et al (2008) Paraventricular nucleus is involved in the central pathway of cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats. Exp Physiol 93:746–753
Zheng H, Li YF, Wang W, Patel KP (2009) Enhanced angiotensin-mediated excitation of renal sympathetic nerve activity within the paraventricular nucleus of anesthetized rats with heart failure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R1364–R1374
Gan XB, Duan YC, Xiong XQ et al (2011) Inhibition of cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex and sympathetic activity by baroreceptor and vagal afferent inputs in chronic heart failure. PLoS ONE 6:e25784
Shi Z, Chen AD, Xu Y et al (2009) Long-term administration of tempol attenuates postinfarct ventricular dysfunction and sympathetic activity in rats. Pflugers Arch 458:247–257
Wang HJ, Zhang F, Zhang Y, Gao XY, Wang W, Zhu GQ (2005) AT1 receptor in paraventricular nucleus mediates the enhanced cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats with chronic heart failure. Auton Neurosci 121:56–63
Zhu GQ, Gao L, Patel KP, Zucker IH, Wang W (2004) ANG II in the paraventricular nucleus potentiates the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats with heart failure. J Appl Physiol 97:1746–1754
Gao L, Wang WZ, Wang W, Zucker IH (2008) Imbalance of angiotensin type 1 receptor and angiotensin II type 2 receptor in the rostral ventrolateral medulla: potential mechanism for sympathetic overactivity in heart failure. Hypertension 52:708–714
Gao L, Wang W, Li YL et al (2004) Superoxide mediates sympathoexcitation in heart failure: roles of angiotensin II and NAD(P)H oxidase. Circ Res 95:937–944
Liu D, Gao L, Roy SK, Cornish KG, Zucker IH (2008) Role of oxidant stress on AT1 receptor expression in neurons of rabbits with heart failure and in cultured neurons. Circ Res 103:186–193
Fahim M, Gao L, Mousa TM, Liu D, Cornish KG, Zucker IH (2012) Abnormal baroreflex function is dissociated from central angiotensin II receptor expression in chronic heart failure. Shock 37:319–324
Michelini LC, Bonagamba LG (1990) Angiotensin II as a modulator of baroreceptor reflexes in the brainstem of conscious rats. Hypertension 15:I45–I50
Wang WZ, Gao L, Pan YX, Zucker IH, Wang W (2007) AT1 receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarii mediate the interaction between the baroreflex and the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in anesthetized rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292:R1137–R1145
Mangiapane ML, Simpson JB (1980) Subfornical organ lesions reduce the pressor effect of systemic angiotensin II. Neuroendocrinology 31:380–384
Gutman MB, Ciriello J, Mogenson GJ (1988) Effects of plasma angiotensin II and hypernatremia on subfornical organ neurons. Am J Physiol 254:R746–R754
Fink GD, Bruner CA, Mangiapane ML (1987) Area postrema is critical for angiotensin-induced hypertension in rats. Hypertension 9:355–361
Matsukawa S, Reid IA (1990) Role of the area postrema in the modulation of the baroreflex control of heart rate by angiotensin II. Circ Res 67:1462–1473
Otsuka A, Barnes KL, Ferrario CM (1986) Contribution of area postrema to pressor actions of angiotensin II in dog. Am J Physiol 251:H538–H546
Davern PJ, Head GA (2007) Fos-related antigen immunoreactivity after acute and chronic angiotensin II-induced hypertension in the rabbit brain. Hypertension 49:1170–1177
Ferguson AV, Bains JS (1997) Actions of angiotensin in the subfornical organ and area postrema: implications for long term control of autonomic output. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 24:96–101
Moretti JL, Burke SL, Davern PJ, Evans RG, Lambert GW, Head GA (2012) Renal sympathetic activation from long-term low-dose angiotensin II infusion in rabbits. J Hypertens 30:551–560
Kang YM, Ma Y, Zheng JP et al (2009) Brain nuclear factor-kappa B activation contributes to neurohumoral excitation in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 82:503–512
LaGrange LP, Toney GM, Bishop VS (2003) Effect of intravenous angiotensin II infusion on responses to hypothalamic PVN injection of bicuculline. Hypertension 42:1124–1129
Ramsay DJ, Keil LC, Sharpe MC, Shinsako J (1978) Angiotensin II infusion increases vasopressin, ACTH, and 11-hydroxycorticosteroid secretion. Am J Physiol 234:R66–R71
Brooks VL, Klingbeil CK, Quillen EW, Keil LC, Reid IA (1989) Effect of baroreceptor denervation on vasopressin and cortisol responses to angiotensin II infusion in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol 257:R1175–R1181
Stanley JR, Giammattei CE, Sheikh AU, Green JL, Zehnder T, Rose JC (1997) Effects of chronic infusion of angiotensin II on renin and blood pressure in the late-gestation fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol 176:931–937
Roth RH (1972) Action of angiotensin on adrenergic nerve endings: enhancement of norepinephrine biosynthesis. Fed Proc 31:1358–1364
Boadle MC, Hughes J, Roth RH (1969) Angiotensin accelerates catecholamine biosynthesis in sympathetically innervated tissues. Nature 222:987–988
Palaic D, Khairallah PA (1967) Inhibition of noradrenaline uptake by angiotensin. J Pharm Pharmacol 19:396–397
Stegbauer J, Kuczka Y, Vonend O et al (2008) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase is predominantly involved in angiotensin II modulation of renal vascular resistance and norepinephrine release. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R421–R428
Gironacci MM, Lorenzo PS, Adler-Graschinsky E (1997) Possible participation of nitric oxide in the increase of norepinephrine release caused by angiotensin peptides in rat atria. Hypertension 29:1344–1350
Stegbauer J, Vonend O, Habbel S et al (2005) Angiotensin II modulates renal sympathetic neurotransmission through nitric oxide in AT2 receptor knockout mice. J Hypertens 23:1691–1698
Stegbauer J, Oberhauser V, Vonend O, Rump LC (2004) Angiotensin-(1–7) modulates vascular resistance and sympathetic neurotransmission in kidneys of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Cardiovasc Res 61:352–359
Stegbauer J, Vonend O, Oberhauser V, Sellin L, Rump LC (2005) Angiotensin II receptor modulation of renal vascular resistance and neurotransmission in young and adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. Kidney Blood Press Res 28:20–26
Tanioka H, Nakamura K, Fujimura S et al (2002) Facilitatory role of NO in neural norepinephrine release in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 282:R1436–R1442
Clemson B, Gaul L, Gubin SS et al (1994) Prejunctional angiotensin II receptors. Facilitation of norepinephrine release in the human forearm. J Clin Invest 93:684–691
Li YL, Xia XH, Zheng H et al (2006) Angiotensin II enhances carotid body chemoreflex control of sympathetic outflow in chronic heart failure rabbits. Cardiovasc Res 71:129–138
Li YL, Gao L, Zucker IH, Schultz HD (2007) NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide anion mediates angiotensin II-enhanced carotid body chemoreceptor sensitivity in heart failure rabbits. Cardiovasc Res 75:546–554
Li YL, Li YF, Liu D et al (2005) Gene transfer of neuronal nitric oxide synthase to carotid body reverses enhanced chemoreceptor function in heart failure rabbits. Circ Res 97:260–267
Schultz HD, Li YL (2007) Carotid body function in heart failure. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 157:171–185
Guild SJ, McBryde FD, Malpas SC, Barrett CJ (2012) High dietary salt and angiotensin II chronically increase renal sympathetic nerve activity: a direct telemetric study. Hypertension 59:614–620
Head GA, Saigusa T, Mayorov DN (2002) Angiotensin and baroreflex control of the circulation. Braz J Med Biol Res 35:1047–1059
Turini GA, Brunner HR, Gribic M, Waeber B, Gavras H (1979) Improvement of chronic congestive heart-failure by oral captopril. Lancet 1:1213–1215
Dibner-Dunlap ME, Smith ML, Kinugawa T, Thames MD (1996) Enalaprilat augments arterial and cardiopulmonary baroreflex control of sympathetic nerve activity in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 27:358–364
Dietz R, Waas W, Susselbeck T, Willenbrock R, Osterziel KJ (1993) Improvement of cardiac function by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition. Sites of action. Circulation 87:IV108–IV116
Gilbert EM, Sandoval A, Larrabee P, Renlund DG, O’Connell JB, Bristow MR (1993) Lisinopril lowers cardiac adrenergic drive and increases beta-receptor density in the failing human heart. Circulation 88:472–480
Hikosaka M, Yuasa F, Yuyama R et al (2002) Candesartan and arterial baroreflex sensitivity and sympathetic nerve activity in patients with mild heart failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 40:875–880
Gottlieb SS, Dickstein K, Fleck E et al (1993) Hemodynamic and neurohormonal effects of the angiotensin II antagonist losartan in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 88:1602–1609
Hamroff G, Katz SD, Mancini D et al (1999) Addition of angiotensin II receptor blockade to maximal angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition improves exercise capacity in patients with severe congestive heart failure. Circulation 99:990–992
Chrysant SG (2008) Angiotensin II receptor blockers in the treatment of the cardiovascular disease continuum. Clin Ther 30(Pt 2):2181–2190
Guthrie R (2009) Recent advances in cardiovascular risk reduction: implications of ONTARGET. Clin Cornerstone 9(Suppl 3):S18–S26
Zong WN, Yang XH, Chen XM et al (2011) Regulation of angiotensin-(1–7) and angiotensin II type 1 receptor by telmisartan and losartan in adriamycin-induced rat heart failure. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:1345–1350
Sharma NM, Zheng H, Mehta PP, Li YF, Patel KP (2011) Decreased nNOS in the PVN leads to increased sympathoexcitation in chronic heart failure: role for CAPON and Ang II. Cardiovasc Res 92:348–357
DiBona GF, Jones SY, Sawin LL (1998) Angiotensin receptor antagonist improves cardiac reflex control of renal sodium handling in heart failure. Am J Physiol 274:H636–H641
Grassi G, Cattaneo BM, Seravalle G et al (1997) Effects of chronic ACE inhibition on sympathetic nerve traffic and baroreflex control of circulation in heart failure. Circulation 96:1173–1179
DiBona GF, Sawin LL (2003) Losartan corrects abnormal frequency response of renal vasculature in congestive heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H1857–H1863
Acknowledgments
This work is funded by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council (540404, 1021416) and the BUPA Foundation. JG holds a Practitioner Fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia (1019921) and a Senior Clinical Research Fellowship from the Queensland Government. SWS is supported by a NHMRC Training Research Fellowship (1016349).
Conflict of interest
Drs. Yutang Wang, Sai-Wang Seto and Jonathan Golledge have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Seto, SW. & Golledge, J. Angiotensin II, sympathetic nerve activity and chronic heart failure. Heart Fail Rev 19, 187–198 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-012-9368-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-012-9368-1