Abstract
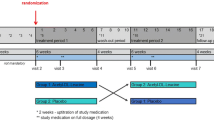
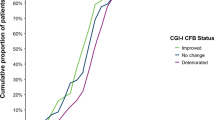
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of idebenone on neurological function as assessed by ICARS and FARS neurological rating scales in pediatric Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) patients. Sixty-eight pediatric patients were enrolled in an open-label extension study (IONIA-E) where patients received idebenone (Catena®, 150 mg film-coated tablets) at a weight-adjusted dose of 1,350/2,250 mg/day for 12 months after patients had completed a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (IONIA) receiving either idebenone at a weight-adjusted dose of 450/900 or 1,350/2,250 mg/day or placebo for 6 months. Changes in ICARS and FARS total scores and subscores were recorded for the 12-month IONIA-E study and for the 18-month combined IONIA and IONIA-E study period. Data analyzed by a mixed-model repeated-measures ANCOVA relative to baseline resulted in least square means for the change in ICARS for the IONIA-E study of +0.98 points (SEM 0.73; p = 0.180), indicating a trend for worsening. However, combined with the IONIA study the change was −1.03 ± 0.68 points (p = 0.132), indicating a trend for improvement in neurological function over the 18-month period. Importantly, patients who received idebenone 1,350/2,250 mg/day over this period significantly improved in neurological function (change in ICARS: −3.02 ± 1.22, p = 0.014). The improvement in neurological function over time was best seen when the posture and stance subscore was excluded from the analysis. Comparable data were obtained with the FARS. The findings of the open-label IONIA-E study combined with the double-blind IONIA study indicate that idebenone at a dose of 1,350/2,250 mg/day may offer a therapeutic benefit to pediatric FRDA patients by stabilizing the overall neurological function and improving fine motor skills and speech.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klockgether T, Lüdtke R, Kramer B et al (1998) The natural history of degenerative ataxia: a retrospective study in 446 patients. Brain 121:589–600
Durr A, Cossee M, Agid Y et al (1996) Clinical and genetic abnormalities in patients with Friedreich’s ataxia. N Engl J Med 335:1169–1175
Schulz JB, Boesch S, Bürk K et al (2009) Diagnosis and treatment of Friedreich ataxia: a European perspective. Nat Rev Neurol 5:222–234
Harding AE (1981) Friedreich’s ataxia: a clinical and genetic study of 90 families with an analysis of early diagnostic criteria and interfamilial clustering of clinical features. Brain 104:589–620
Tsou AY, Paulsen EK, Lagedrost SJ et al (2011) Mortality in Friedreich ataxia. J Neurol Sci (in press)
Santos R, Lefevre S, Sliwa D et al (2010) Friedreich ataxia: molecular mechanism, redox considerations, and therapeutic opportunities. Antiox Redox Signal 13:651–690
Tonon C, Lodi R (2008) Idebenone in Friedreich’s ataxia. Expert Opin Pharmacother 9:2327–2337
Schulz JB, Di Prospero NA, Fischbeck K (2009) Clinical experience with high dose idebenone in Friedreich ataxia. J Neurol 256(Suppl 1):42–45
Di Prospero NA, Baker A, Jeffries N et al (2007) Neurological effects of high-dose idebenone in patients with Friedreich’s ataxia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 6(10):878–886
Artuch R, Aracil A, Mas A et al (2002) Friedreich’s ataxia: idebenone treatment in early stage patients. Neuropediatrics 33(4):190–193
Arnold P, Boulat O, Maire R et al (2006) Expanding view of phenotype and oxidative stress in Friedreich’s ataxia patients with and without idebenone. Schweizer Archiv für Neurology und Psychiatrie 157:169–176
Pineda M, Arpa J, Montero R et al (2008) Idebenone treatment in paediatric and adult patients with Friedreich ataxia: long-term follow-up. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 12(6):470–475
Lynch DR, Perlman SL, Meier T (2010) A phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of idebenone in Friedreich Ataxia. Arch Neurol 67(8):941–947
Trouillas P, Takayanagi T, Hallett M et al (1997) International cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale for pharmacological assessment of the cerebellar syndrome. J Neurol Sci 145:205–211
Subramony SH, May W, Lynch D et al (2005) Measuring Friedreich ataxia: interrater reliability of a neurologic rating scale. Neurology 64:1261–1262
Folker J, Murdoch B, Cahill L et al (2010) Dysarthria in Friedreich’s ataxia: a perceptual analysis. Folia Phoniatr Logop 62:97–103
Singh A, Epstein E, Myers LM et al (2010) Clinical measures of dysarthria in Friedreich ataxia. Mov Disord 25:108–121
Fahey MC, Corben L, Collins V et al (2007) How is disease progress in Friedreich’s ataxia best measured? A study of four rating scales. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:411–413
Ribai P, Pousset F, Tanguy ML et al (2007) Neurological, cardiological, and oculomotor progression in 104 patients with Friedreich ataxia during long-term follow-up. Arch Neurol 64:558–564
Sival DA, Brunt ER (2009) The international cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale shows strong age-dependency in children. Dev Med Child Neurol 51:571–572
Friedman LS, Farmer JM, Perlman S et al (2010) Measuring the rate of progression in Friedreich ataxia: implications for clinical trial design. Mov Disord 25:426–432
Di Prospero NA, Sumner CJ, Penzak SR et al (2007) Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of high-dose idebenone in patients with Friedreich ataxia. Arch Neurol 64:803–808
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge assistance of the clinical coordinators of the study: Lisa Friedman, Erin Paulsen, Lynn Kessler, Sharaone Trifskin, and Bonnie Johnson. Statistical analyses were conducted by an independent statistician, Britt-Marie Lindström, 4Pharma, Sweden. The present study was sponsored by Santhera Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Lynch has received grant funding for other projects from the National Institutes of Health, the Muscular Dystrophy Association, the Friedreich Ataxia Research Alliance and Penwest Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Perlman has also received grant funding for other projects from the National Institutes of Health, the HighQ/CHDI Foundation, the National Ataxia Foundation, the Muscular Dystrophy Association, the Friedreich Ataxia Research Alliance, and Edison Pharmaceuticals. Drs. Meier, Coppard and Rummey are employees of Santhera Pharmaceuticals.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meier, T., Perlman, S.L., Rummey, C. et al. Assessment of neurological efficacy of idebenone in pediatric patients with Friedreich's ataxia: data from a 6-month controlled study followed by a 12-month open-label extension study. J Neurol 259, 284–291 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6174-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6174-y