Abstract
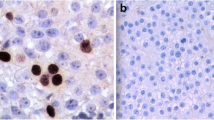
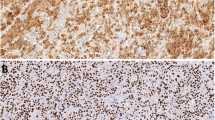
Hyperparathyroidism 2 (HRPT2) gene mutations underlie hereditary and sporadic forms of primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT), and the encoded product parafibromin has been established as a marker for facilitating parathyroid tumour classification. HRPT2 mutations and reduced nuclear expression of parafibromin are readily observed in parathyroid carcinomas but rarely in benign tumours, thereby aiding the identification of malignant PHPT. Recently, parafibromin has been shown to localize to the nucleolar compartment, and nucleolar parafibromin exhibits tumour-suppressive properties in vitro. In this study, nucleolar parafibromin immunoreactivity was assessed by high-power magnification microscopy in 82 parathyroid tumours previously analysed for nuclear parafibromin, including 23 carcinomas, 16 atypical adenomas, and 43 adenomas. Absent nucleolar expression was evident in three carcinomas and in one atypical adenoma, which also showed expression of nuclear parafibromin in all or subsets of the tumour cells. All three carcinomas carried HRPT2-inactivating mutations predicted to abolish the three nucleolar localization signals of parafibromin. The demonstrated absence of nucleolar parafibromin in three carcinomas with HRPT2 mutations suggests that parafibromin exhibits nucleolar tumour suppressor properties also in vivo, and disruption of nucleolar localization might propel parathyroid tumorigenesis independent of nuclear parafibromin expression. The loss of nucleolar staining in the presence of nuclear parafibromin suggests that parafibromin immunoreactivity should also be assessed in the nucleoli, as the sensitivity for the detection of malignant and atypical PHPT is increased compared to scoring of nuclear parafibromin alone.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carpten JD, Robbins CM, Villablanca A et al (2002) HRPT2, encoding parafibromin, is mutated in hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome. Nat Genet 32:676–680
Howell VM, Haven CJ, Kahnoski K et al (2003) HRPT2 mutations are associated with malignancy in sporadic parathyroid tumours. J Med Genet 40:657–663
Shattuck TM, Välimäki S, Obara T et al (2003) Somatic and germ-line mutations of the HRPT2 gene in sporadic parathyroid carcinoma. N Engl J Med 349:1722–1729
Tan MH, Morrison C, Wang P et al (2004) Loss of parafibromin immunoreactivity is a distinguishing feature of parathyroid carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:6629–6637
Juhlin CC, Villablanca A, Sandelin K et al (2007) Parafibromin immunoreactivity: its use as an additional diagnostic marker for parathyroid tumor classification. Endocr Relat Cancer 14:501–512
Sandelin K, Tullgren O, Farnebo LO (1994) Clinical course of metastatic parathyroid cancer. World J Surg 18:594–598, discussion 599
Ippolito G, Palazzo FF, Sebag F et al (2007) Intraoperative diagnosis and treatment of parathyroid cancer and atypical parathyroid adenoma. Br J Surg 94:566–570
Gill AJ, Clarkson A, Gimm O et al (2006) Loss of nuclear expression of parafibromin distinguishes parathyroid carcinomas and hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor (HPT-JT) syndrome-related adenomas from sporadic parathyroid adenomas and hyperplasias. Am J Surg Pathol 30:1140–1149
Juhlin C, Larsson C, Yakoleva T et al (2006) Loss of parafibromin expression in a subset of parathyroid adenomas. Endocr Relat Cancer 13:509–523
Fernandez-Ranvier GG, Khanafshar E, Tacha D et al (2009) Defining a molecular phenotype for benign and malignant parathyroid tumors. Cancer 115:334–344
Howell VM, Gill A, Clarkson A et al (2009) Accuracy of combined protein gene product 9.5 and parafibromin markers for immunohistochemical diagnosis of parathyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:434–441
Juhlin CC, Haglund F, Villablanca A et al (2009) Loss of expression for the Wnt pathway components adenomatous polyposis coli and glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta in parathyroid carcinomas. Int J Oncol 34:481–492
Hahn MA, Marsh DJ (2007) Nucleolar localization of parafibromin is mediated by three nucleolar localization signals. FEBS Lett 581:5070–5074
Panicker LM, Zhang JH, Dagur PK et al (2010) Defective nucleolar localization and dominant interfering properties of a parafibromin L95P missense mutant causing the hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:513–524
Juhlin CC, Nilsson IL, Johansson K et al (2010) Parafibromin and APC as screening markers for malignant potential in atypical parathyroid adenomas. Endocr Pathol 21:166–177
Itahana K, Bhat KP, Jin A et al (2003) Tumor suppressor ARF degrades B23, a nucleolar protein involved in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. Mol Cell 12:1151–1164
Frescas D, Guardavaccaro D, Bassermann F et al (2007) JHDM1B/FBXL10 is a nucleolar protein that represses transcription of ribosomal RNA genes. Nature 450:309–313
Montanaro L, Treré D, Derenzini M (2008) Nucleolus, ribosomes, and cancer. Am J Pathol 173:301–310
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Ingo Leibiger and Barbara Leibiger for proficient help in acquiring images from previous live cell imaging experiments. The study was financially supported by the Swedish Cancer Society, the Swedish Research Council, the Cancer Society in Stockholm, the Gustav V Jubilee Foundation, the Göran Gustafsson Foundation for Research on Natural Sciences and Medicine, the Stockholm County Council and Karolinska Institutet.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juhlin, C.C., Haglund, F., Obara, T. et al. Absence of nucleolar parafibromin immunoreactivity in subsets of parathyroid malignant tumours. Virchows Arch 459, 47–53 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-010-1032-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-010-1032-3