Abstract
Background
Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection (UEMR) without submucosal injection is a novel endoscopic procedure. It is not known if UEMR can be easily taught and learned, and the efficacy and safety of UEMR has not been demonstrated at multiple medical centers. Our aims were to demonstrate that (1) UEMR is a technique that can be easily learned by an endoscopist trained in traditional EMR, (2) endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) may not be required before UEMR, and (3) UEMR is an efficacious and safe method for resection of large or flat neoplastic colorectal lesions.
Methods
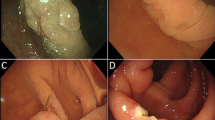
An experienced interventional endoscopist began performing UEMR after observing UEMR procedures. Colorectal UEMR was performed using a pediatric colonoscope with a cap, a waterjet, and a ‘duck-bill’ snare using blended current. Submucosal injection was not used. Patient data were collected prospectively.
Results
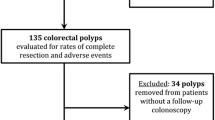
A total of 21 patients (17 men, mean age 64.9 years, range 51–83) referred for polypectomy of large colorectal lesions underwent UEMR. A total of 43 colorectal lesions with a mean size of 20 mm (range 8–50) were resected by UEMR. Lesions were found in the right colon (N = 16), transverse colon (N = 5), left colon (N = 19), and rectum (N = 3). Pathology demonstrated tubular adenoma (N = 29), tubulovillous adenoma (N = 5), high-grade dysplasia (N = 3), serrated sessile adenoma without dysplasia (N = 3), and non-neoplastic tissue (N = 3). EUS was used in only two cases of rectal neoplasia (4.7 %). Of the UEMRs, 97.7 % were successful with complete resection of colorectal polyps. The only adverse event was one case (2.3 %) of delayed post-UEMR bleeding.
Conclusions
UEMR was easily learned by an endoscopist already skilled in conventional EMR. EUS may not be required prior to most UEMR procedures. UEMR appears to be an efficacious and safe alternative to traditional EMR or ESD for large or flat colorectal neoplasms.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMR:
-
Endoscopic mucosal resection
- ESD:
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- UEMR:
-
Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection
- EUS:
-
Endoscopic ultrasound
- GEE:
-
Generalized estimating equation
- APC:
-
Argon plasma coagulation
- EPMR:
-
Endoscopic piecemeal mucosal resection
- TA:
-
Tubular adenoma
- NBI:
-
Narrow-band imaging
- TVA:
-
Tubulovillous adenoma
- SSA:
-
Serrated sessile adenoma
References
Wang AY, Ahmad NA, Zaidman JS, Brensinger CM, Lewis JD, Long WB, Kochman ML, Ginsberg GG (2008) Endoluminal resection for sessile neoplasia in the GI tract is associated with a low recurrence rate and a high 5 years survival rate. Gastrointest Endosc 68:160–169
Wang AY, Emura F, Oda I, Cox DG, Kim HS, Yeaton P (2010) Endoscopic submucosal dissection with electrosurgical knives in a patient on aspirin therapy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 72:1066–1071
Teoh AY, Chiu PW, Wong SK, Sung JJ, Lau JY, Ng EK (2010) Difficulties and outcomes in starting endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc 24:1049–1054
Binmoeller KF, Weilert F, Shah J, Bhat Y, Kane S (2012) ‘Underwater’ EMR without submucosal injection for large sessile colorectal polyps (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 75:1086–1091
Leung FW, Amato A, Ell C, Friedland S, Harker JO, Hsieh YH, Leung JW, Mann SK, Paggi S, Pohl J, Radaelli F, Ramirez FC, Siao-Salera R, Terruzzi V (2012) Water-aided colonoscopy: a systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc 76:657–666
Henry ZH, Yeaton P, Shami VM, Kahaleh M, Patrie JT, Cox DG, Peura DA, Emura F, Wang AY (2010) Meshed capillary vessels found on narrow-band imaging without optical magnification effectively identifies colorectal neoplasia: a North American validation of the Japanese experience. Gastrointest Endosc 72:118–126
Hardin JW, Hilbe J (2003) Generalized estimating equations. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, FL
No authors listed (2003) The Paris endoscopic classification of superficial neoplastic lesions: esophagus, stomach, and colon: November 30 to December 1, 2002. Gastrointest Endosc 58(6):S3–43
Waxman I (2006) EUS and EMR/ESD: is EUS in patients with Barrett’s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia or intramucosal adenocarcinoma necessary prior to endoscopic mucosal resection? Endoscopy 38(1):S2–S4
Choi J, Kim SG, Im JP, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS (2010) Is endoscopic ultrasonography indispensable in patients with early gastric cancer prior to endoscopic resection? Surg Endosc 24:3177–3185
Ahmad NA, Kochman ML, Long WB, Furth EE, Ginsberg GG (2002) Efficacy, safety, and clinical outcomes of endoscopic mucosal resection: a study of 101 cases. Gastrointest Endosc 55:390–396
Tajika M, Niwa Y, Bhatia V, Kondo S, Tanaka T, Mizuno N, Hara K, Hijioka S, Imaoka H, Ogura T, Haba S, Yamao K (2011) Comparison of endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for large colorectal tumors. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:1042–1049
Sakamoto T, Matsuda T, Otake Y, Nakajima T, Saito Y (2012) Predictive factors of local recurrence after endoscopic piecemeal mucosal resection. J Gastroenterol 47:635–640
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Dr. Kenneth F. Binmoeller for his contributions to the field of endoscopy and for teaching Dr. Wang the UEMR technique.
Disclosures
Andrew Y. Wang, Mary M. Flynn, James T. Patrie, Dawn G. Cox, Wissam Bleibel, James A. Mann, Bryan G. Sauer, Vanessa M. Shami have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose with respect to this manuscript. This work was not supported by any external grants or funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (WMV 25,111 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (WMV 66,439 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (WMV 10,710 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, A.Y., Flynn, M.M., Patrie, J.T. et al. Underwater endoscopic mucosal resection of colorectal neoplasia is easily learned, efficacious, and safe. Surg Endosc 28, 1348–1354 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3297-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3297-5