Abstract
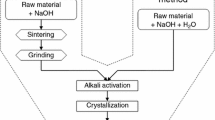
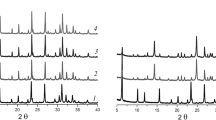
The results of investigation of catalysts based on natural zeolite in comparison with synthetic ZSM-5 zeolite used in reduction of nitrogen oxides and conversion of carbon monoxide are presented. It was found that rearrangement of the crystal structure of natural zeolite begins upon heating it above 500 °C in air. The structure of natural zeolite has been improved by introduction of various modifiers and selection of thermal regime of samples training. It has been shown that developed compositions of press-mass for preparation of carriers for gas purification catalysts in the form of granules and tablets satisfy the requirements on ductility and mechanical strength. The efficiency of synthesized granular and block Cu–Ce, Cu–Ni–Cr, Ti–V, Ti–VW, and TiO2–V2O5 catalysts based on natural and synthetic zeolites was determined in conversion of CO and nitrogen oxides. The results of X-ray structure analysis of clinoptilolite of the Republic of Kazakhstan deposits—Chankanai and Taizhuzgen—are represented in comparison with synthetic ZSM-5 zeolite. The paper also comprises data about their thermal stability, ductility, and strength of compositions on their base. Metals particles morphology and dispersity are studied by the method of electronic microscopy. These particles were used as active components of synthesized catalysts.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimkhan AM (2012) Structural and ion-exchange properties of natural zeolite. Ion Exch Technol. doi:10.5772/51682
Arcoya A, Gonzalez JA, Travieso N, Seoane XL (1994) Physicochemical and catalytic properties of a modified natural clinoptilolite. Clay Miner 29:123–131
Bamniya B, Kapoor C, Kapoor K (2011) Searching for efficient sink for air pollutants: studies on Mangifera indica L. Clean Technol Environ Policy 14:107–114
Canafoglia ME, Lick ID, Ponzi EN, Botto IL (2009) Natural materials modified with transition metals of the cobalt group: feasibility in catalysis. Journal Argent Chem Soc 97:58–68
Da Silva JD, Oliveira CC (2013) Mathematical modelling for the adsorption process of CO2 in nanopores of catalytic particles in a fixed bed reactor using numeral inverse laplace transform. Chem Eng Trans 35:829–834
Hagiwara K, Ebihara T, Yamada H, Shibuya T, Naito J, Ozawa S, Nakata S (2002) Dealumination of USY zeolites by thermal treatment. J Jpn Petrol Inst 45:45–52
Hagiwara K, Ebihara T, Urasato N, Ozawa S, Nakata S (2003) Effect of vanadium on USY zeolite destruction in the presence of sodium ions and steam-studies by solid-state NMR. Appl Catal A 249:213–228
Koutsonikolas DE, Kaldis SP, Pantoleontos GT, Zaspalis VT, Sakellaropoulos GP (2013) Techno-economic assessment of polymeric, ceramic and metallic membranes integration in an advanced IGCC process for H2 production and CO2 capture. Chem Eng Trans 35:715–720
Krylov OB, Matyshak VA (1996) Promezhutochnye coedineniya v geterogennom katalize (Intermediate compounds in heterogeneous catalysis). Nauka, Moscow (in Russian)
Li Y, Wu D, Zhang J, Chang L, Wu D, Fang Z, Shi Y (2000) Measurement and statistics of single pellet mechanical strength of differently shaped catalysts. Powder Technol 113:176–184
Mansouri N, Rikhtegar N, Panahi HA, Atabi F, Shahraki BK (2013) Porosity, characterization and structural properties of natural zeolite– clinoptilolite—as a sorbent. Environ Prot Eng 39:139–152
Mat Rosid SJ, Wan Abu Bakar WA, Ali R (2015) Physicochemical study of supported cobalt–lanthanum oxide-based catalysts for Co2/H2 methanation reaction. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:257–264
Mihajlović MT, Lazarević SS, Janković-Častvan IM, Kovač J, Jokić BM, Janaćković DT, Petrović RD (2015) Kinetics, thermodynamics, and structural investigations on the removal of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ from multicomponent solutions onto natural and Fe(III)-modified zeolites. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:407–419
Mikulčić H, Vujanović M, Markovska N, Filkoski RV, Ban M, Duić N (2013) CO2 Emission reduction in the cement industry. Chem Eng Trans 35:703–708
Mukhlyonov IP, Dobkina EI, Derjuzhkina VI, Soroko VE (1989) Catalyst technology. Himiya, Leningrad (in Russian)
Novikova L, Belchinskaya L, Roessner F, Alsawalha M (2013) Characterization of surface acidity and catalytic ability of natural clay minerals by means of test catalytic reaction. Acta Geodyn Geomater 10:475–484
Ono A, Abe M, Kato S, Ogasawara M, Wakabayashi T, Nakahara Y, Nakata S (2011) NO reduction property of apatite-type La8A2Si6O26 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba) supported Pt catalyst. Appl Catal B 103:149–153
Palma V, Barba D, Ciambelli P (2013) Selective oxidation of H2S to sulphur from biogas on V2O5/CeO2 catalysts. Chem Eng Trans 32:631–636
Panepinto D, Brizio E, Genon G (2014) Atmospheric pollutants and air quality effects: limitation costs and environmental advantages (a cost-benefit approach). Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:1805–1813
Rabo J (1980) Himiya tseolitov i kataliz na tsiolitah (Zeolites chemistry and catalysis on zeolites). Mir, Moscow (in Russian)
Regalbuto J (2006) Catalyst preparation science and engineering. The University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago
Reşitoğlu İA, Altinişik K, Keskin A (2015) The pollutant emissions from diesel-engine vehicles and exhaust aftertreatment systems. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:15–27
Rikhtegar N, Panahi HA, Mansouri N (2013) Chemical modification and characterization of clinoptilolite by 1,3-phenylenediamine as a sorbent for the removal of NO2. Int J Appl Innov Eng Manag 2:182–189
Rivera A, Rodriguez-Fuentes G, Altshuler E (2000) Time evolution of a natural clinoptilolite in aqueous medium: conductivity and pH experiments. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 40:173–179
Schwarz JA, Contescu C, Contescu A (1995) Methods for preparation of catalytic materials. Chem Rev 95:477–510
Sellitto MA, Borchardt M, Pereira GM, Bubicz ME (2015) Tool for environmental performance assessment of city bus transit operations: case studies. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:1053–1064
Tatsumi T, Tanaka Y, Nakata S (1999) Mechanical stability of mesoporous materials, MCM-48 and MCM-41. J Porous Mater 6:13–17
Vinodh S, Jayakrishna K, Joy D (2011) Environmental impact assessment of an automotive component using eco-indicator and CML methodologies. Clean Technol Environ Policy 14:333–344
Wdowin M, Franus M, Panek R, Badura L, Franus W (2014) The conversion technology of fly ash into zeolites. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16:1217–1223
Wu D, Zhou J, Li Y (2007) Mechanical strength of solid catalysts: recent developments and future prospects. Am Inst Chem Eng J 53:2618–2629
Zaleska A (2008) Doped-TiO2: a review. Recent Pat Eng 2:157–164
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the employees of the IRGETAS regional laboratory of the D. Serikbayev East Kazakhstan State Technical University for their assistance in conducting the physical and chemical research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadenova, M.A., Abdulina, S.A. & Tungatarova, S.A. The use of natural Kazakhstan zeolites for the development of gas purification catalysts. Clean Techn Environ Policy 18, 449–459 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-1018-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-1018-6